
An example of such cost is the cost of material, labour, and overheads employed in manufacturing a table. If it is a period cost, determine if the cost is related to selling the product or the general administration of the company. Terms like administrative indicate that the cost is an administrative cost. A period cost can be termed as any cost that cannot be categorized into prepaid expenses, fixed assets, or inventory. Rather than being a transactional event, this cost is more closely linked with time. Since this cost is mostly charged as an expense all at once, it is appropriate to term it a period expense.
Differences between management and tax accounting
By accurately forecasting Period Costs, businesses can develop realistic budgets and allocate resources effectively. While certain advertising expenses, such as retainer fees for marketing agencies, may be fixed, additional advertising spending may vary based on promotional campaigns and initiatives. Depreciation is another type of period cost, representing the loss in value of fixed assets like machinery and equipment as they wear down over time. Depreciation is considered a Period Cost because it’s incurred over time rather than directly tied to the production of goods or services. Direct Labor, Direct Materials, and Sales Commissions are examples of costs that can be directly allocated.
Managerial Accounting

These costs are integral to understanding the financial landscape of a company and require a detailed examination to appreciate their role in accounting and management. Period costs are expenses that Bookkeeping for Consultants aren’t directly tied to production, and they’re incurred during an accounting period regardless of the volume of goods produced or sold. This means that period costs don’t change with the amount of goods produced or sold. Learn about the concept of period costs in accounting and their significance in finance. Understand how these costs are different from product costs and their impact on financial statements.

What Are Period Costs
This period determines how often you receive your paycheck and also plays a role in determining the amount you contribute towards your health insurance premiums. In the accounting records, the cost of finished products is accumulated in an inventory account – usually “Finished Goods Inventory”. When goods are sold, the cost is transferred from “Finished Goods Inventory” in the balance sheet to “Cost of Sales” (or Cost of Goods Sold) in the income statement.

Importance of Period Costs in Financial Statements
- Understanding these differences is important for performing a detailed financial analysis.
- There is no proper formula to calculate total period costs, and recording period expenses doesn’t follow a set of rules across all areas.
- Period costs encompass a variety of expenses that are essential for the day-to-day operations of a business but are not part of the manufacturing process.
- Fixed costs remain constant for a given tenure, irrespective of the level of output.
- CFI is the global institution behind the financial modeling and valuation analyst FMVA® Designation.
- The manager believes the number of units produced is the activity driver for maintenance costs.
Product costs help you fine-tune the price of each item you sell, ensuring profitability. Period costs guide decisions about how to efficiently rule your small business realm to stay afloat, impacting staffing, advertising, and day-to-day operations. Unlike product costs, period costs don’t linger in the inventory valuation storyline.
Evaluating Profitability
- To overcome these challenges, finance professionals should employ robust cost accounting systems, utilize appropriate cost allocation methods, and consider qualitative factors in their analyses.
- Cost behavior is how a cost reacts to changes in production, usage, or sales quantity.
- As the name suggests, product costs are derived from producing major types of products by the business.
- If you manufacture a product, these costs would include direct materials and labor along with manufacturing overhead.
- This necessitates a thorough analysis of both direct and indirect expenses to determine the minimum price at which a product can be sold without incurring a loss.
When you look at a business’s income statement or a balance sheet, product and period costs show up there, influencing different parts of these financial statements. Understanding the impact of pay periods on your health insurance coverage and benefits enables you to proactively manage your healthcare needs and expenses. It also helps ensure a smooth transition during changes in employment status and allows you to take advantage of period costs any available benefits and contribution opportunities. Understanding the specifics of pay periods in relation to health insurance is important because it affects the timing of your coverage and the amount you pay for your policy.
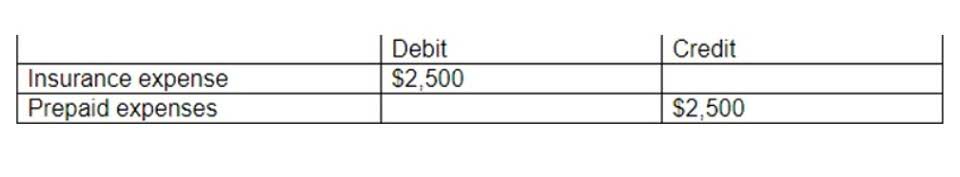
On the other hand, if a cost is linked to a product, inventory, production, or goods and may be incurred over several accounting periods, you may be looking at a product cost. Since product costs are payroll linked to a product, a company can report such costs in the category of cost of goods sold on the income statement. The product costs are the costs incurred by a company directly related to the production of goods. Explore the role of period costs in financial management, from accounting practices to strategic pricing and budgeting, for informed business decisions. Period costs can be a significant portion of a company’s expenses, and they can vary depending on the industry and the size of the business. For instance, a small retail store might have a higher proportion of period costs compared to a large manufacturing company.